Heart flutters could have potential effects on your child. Learn how to spot, manage and treat them in this helpful guide
If you felt like your heart skipped a beat the moment you first set eyes on your child, you’re probably well acquainted with the idea of a fluttering heart. At least figuratively. And yet, on a literal level, when skipped heart beats happen routinely, especially in children, there may be cause for medical attention. The term, in the medical sphere, is known as arrhythmia.
Understanding pediatric arrhythmias
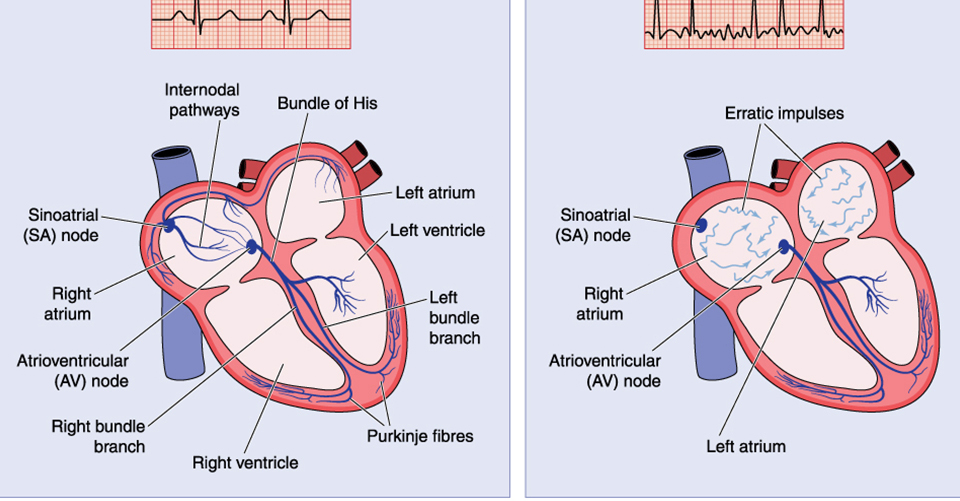
An arrhythmia occurs when abnormal electrical signals transmit through the heart, causing it to pulse either too slowly, too quickly, or sporadically. Resultantly, irregular heart patterns may give rise to reduced blood flow to organs and potentially cause a degree of organ damage.
Causes of pediatric arrhythmia
There are still a lot of unknowns as far as the causes of arrhythmia go. However, some likely triggers include:
- Congenital heart disease or defects
- Genetic heart problems
- Infections or illnesses
- Skewed blood chemical composition
- Intense exercise or emotional experiences
- Structural changes in the heart
- Electrical conduction anomalies
Symptoms of pediatric arrhythmia
Often, arrhythmia is asymptomatic, so a child and their parents may never need to seek a diagnosis or treatment. However, for children who do experience symptoms, these might manifest as:
- Fatigue or weakness
- Fluttering in the heart
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Low blood pressure
- Fainting
- Loss of appetite
These symptoms may overlap with other general health or heart conditions, so if you’re concerned, seeking a diagnosis from a pediatric cardiologist at a specialized children’s heart institute is of the essence.
Diagnosing pediatric arrhythmia
In order to have your child assessed for an arrhythmia, it’s important that you see a pediatric cardiologist, a doctor who specializes in pediatric heart conditions. Your specialist might decide to use one or more tests to evaluate your child. Some of those that might be suggested include:
- Electrocardiogram
- Resting electrocardiogram
- Stress test
- Electrophysiologic study
- Tilt table test
- Echocardiography
- Holter monitoring
Treating pediatric arrhythmia
Arrhythmia spans a spectrum of severity. While some children might experience mild or nonexistent symptoms, others might require treatment. That being said, a treatment plan is developed in accordance with a child’s age, health profile and symptoms. If your pediatric cardiologist thinks that your child requires treatment, the suggested medical intervention might involve one or more of the following:
Medical treatment
A course of medicine that can provide relief and minimize symptoms.
Surgical intervention
A surgery that corrects the rhythmic anomalies in the heart.
Radiofrequency ablation
A catheter that eliminates the tissue responsible for causing abnormal signals in the heart.
Pacemaker
A small electrical aid inserted inside the chest or abdomen. It supplies tiny electrical currents to keep the heartbeat steady, and may be recommended for slow heartbeats.
Electrical cardioversion
An electrical shock, administered by a pediatric cardiologist, that helps reset the heart’s rhythm by correcting its electrical pace.
Implantable cardioverter defibrillator
An aid inserted inside the abdomen or chest to arrest abnormal rhythms. These sometimes also double as pacemakers.
Taking heart in Rainbow Children’s Heart Institute
At Rainbow Children’s Heart Institute, we’re devoted to giving our little hearts the greatest care. Learn more about our pediatric cardiac treatments by visiting our website or consulting with a specialist at our center.
Want a professional diagnosis for your child? Click here to book an appointment with a pediatric cardiologist at Rainbow Children’s Heart Institute.https://www.rainbowchildrensheartinstitute.in/